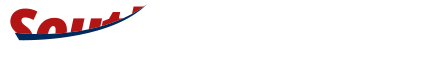Sandwiched between Venezuela and Suriname, the former British colony of Guyana is the only English-speaking country in South America.
Since independence from the UK in 1966, Guyana has seen fierce political rivalry between the two main ethnically-based parties.
Most of the country is covered in tropical rainforest and, despite having rich reserves of bauxite, gold and timber, it has traditionally struggled to overcome poverty and attract investment to bolster its economy.
Guyana’s economy has been undergoing a transformation since the discovery of crude oil in 2015 and commercial drilling in 2019. A century-old border dispute with Venezuela has revived after this discovery of major offshore oil reserves.
CO-OPERATIVE REPUBLIC OF GUYANA: FACTS
- Capital: Georgetown
- Area: 214,970 sq km
- Population: 795,400
- Languages: English, Guyanese Creole, plus others
- Life expectancy: 67 years (men) 73 years (women)
LEADER
President: Irfaan Ali
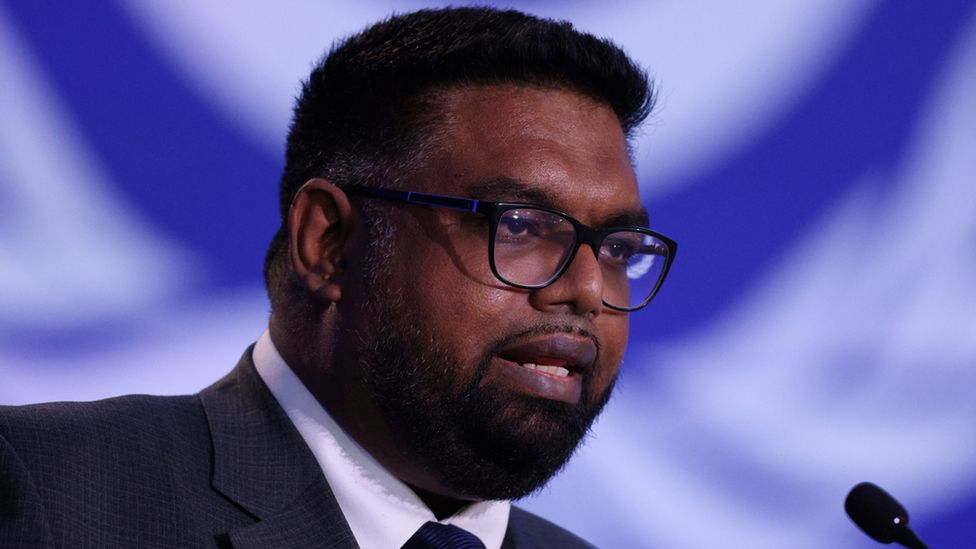

The hotly-disputed March 2020 election was eventually resolved in favour of opposition candidate Irfaan Ali, who became the country’s first Muslim president in August.
A former housing and tourism minister in People’s Progressive Party governments, Mr Ali beat the incumbent president, David Granger of the People’s National Congress, after a full recount amid allegations of government vote-rigging.
A coalition led by the People’s Progressive Party also won a narrow majority in the simultaneous parliamentary election.
President Ali took over not long after the US oil giant Exxon made one of the world’s biggest discoveries of oil in deep waters off Guyana’s coast, which could change the country’s economic prospects dramatically.
MEDIA
The constitution guarantees free speech, although officials are apt to resort to defamation laws, says Reporters Without Borders.
A bill passed in 2017 was criticised for requiring private broadcasters to carry a daily quota of government-chosen output.
There were 576,000 internet users by July 2022, 50.5% of the population. (worldinternetstats.com)
TIMELINE

Some key dates in Guyana’s history:
1300s – Area is first inhabited by semi-nomadic Amerindian tribes, notably Warraus. Christopher Colombus sights Guyana in 1498.
1580 – The Dutch gain a foothold and set up trading posts. From 1620, the Dutch West India Company imports African slaves to work on its sugar plantations.
1780-1813 – Guyana changes hands between the Dutch, French and British.
1814 – Britain occupies Guyana during the Napoleonic Wars and later makes it a the Colony of British Guiana.
1834 – The abolition of slavery leads to indentured workers being brought in from India.
1889 – Venezuela lays claims to two-thirds of Guyana west of the Essequibo river, but international arbitration rules in favour of Guyana in 1899.
1953 – Britain suspends a new constitution and installs an interim administration after the Indo-Guyanese PPP party’s success in the first free elections.
1960 – A new constitution provides full internal self-government, but in 1964 a revolt leads to racial strife and violent riots
1966 – Guyana gains independence.
1978 – Jonestown massacre: Mass suicide by more than 900 members of the People’s Temple religious sect led by Jim Jones.
2015 – Guyana’s multiracial opposition coalition led by David Granger wins the general election, ending 23 years of rule by the Indo-Guyanese PPP party. The PPP returns to power five years later.
2019 – Drilling begins at major offshore oil deposits.
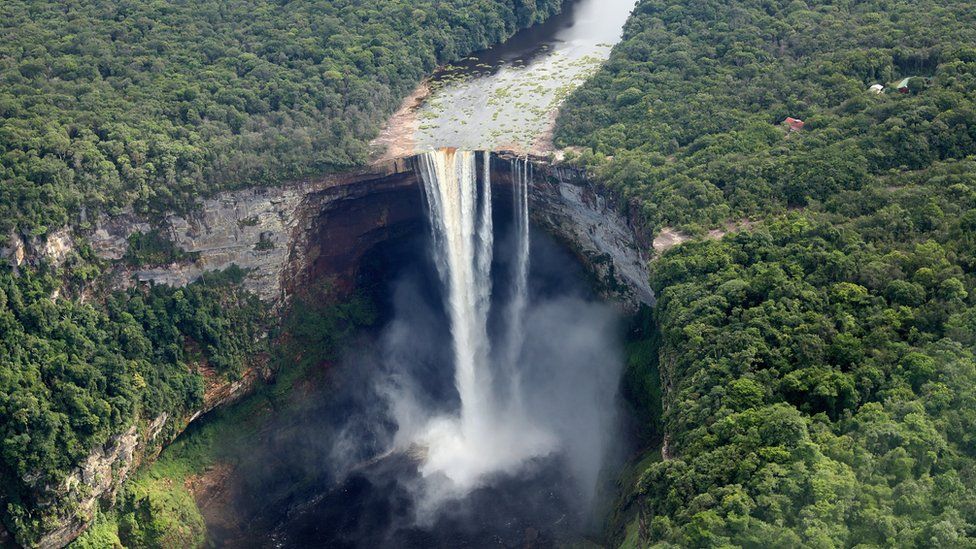

Image caption,Guyana’s spectacular Kaieteur Falls drop for about 220m
Source: BBC